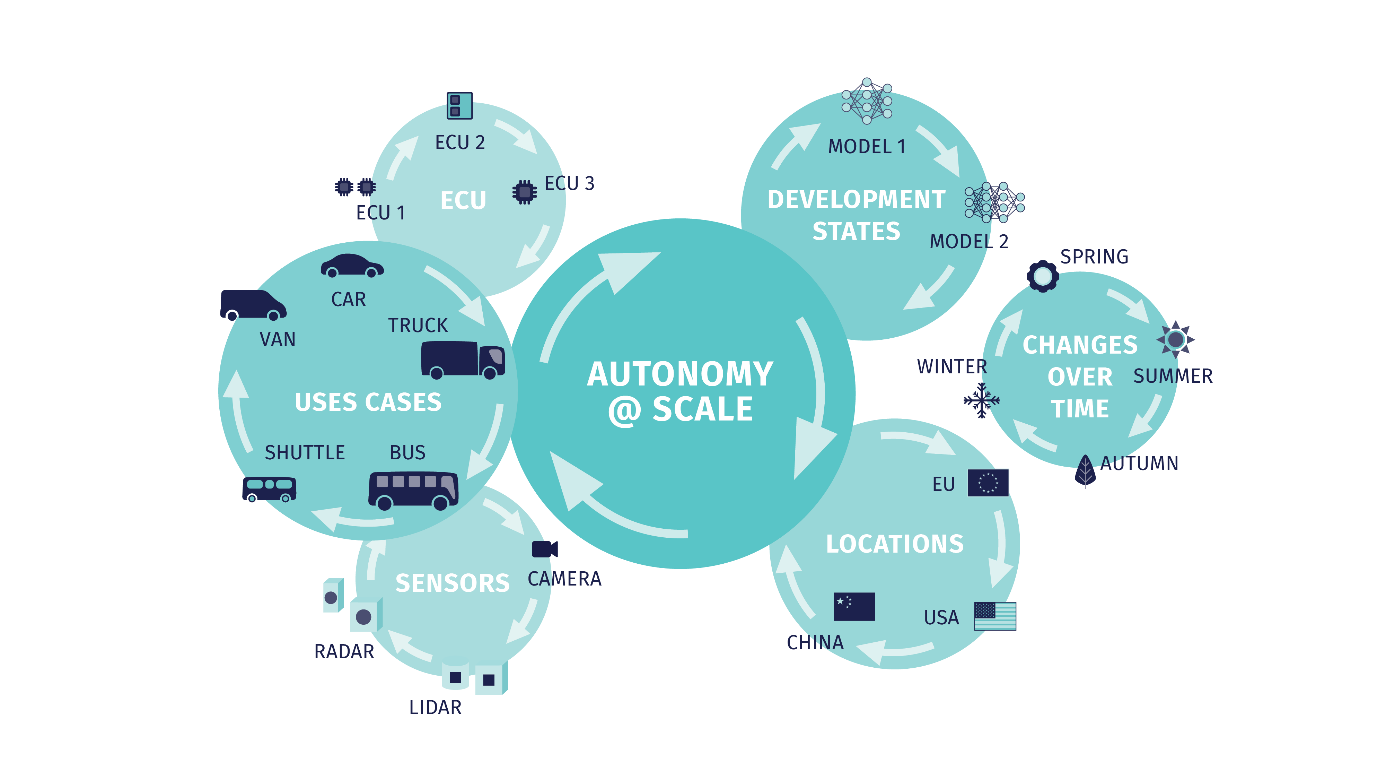
IV2022: Second Workshop on Autonomy@Scale
The IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Society (ITSS) advances the theoretical, experimental, and operational aspects of intelligent transportation systems, including autonomous driving. The Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV 2022) is a premier forum sponsored by the IEEE ITSS in its 33rd edition of the conference this year. This workshop is part of IV 2022 and a follow-up to the first workshop held at IV 2021.